
If you read much about
startup culture or business management, you’ve no doubt come across the terms
“Lean,” “Six Sigma,” and maybe even “Design Thinking.” These are concepts
integral to operations management and concerned with reducing both the amount
of variability and the amount of error or waste that takes place within a given
process or set of procedures.
I recently had the
opportunity to participate in a research project that applied these
methodologies to operating room utilization in a local hospital. As the project
progressed, I reflected on how a similar approach could benefit any manager or
contributor looking to optimize his or her personal efficiency or the
efficiency of a team, department, or agency.
Specifically, this post will
cover two core elements of lean six sigma and how they can be applied by PPC managers
and other digital marketers or directors.
Process (“Value-Stream”) Mapping
The first step is obviously
choosing a starting point. You must consider every process that is completed on
a regular basis and determine which would be most valuable to optimize.
Starting with processes that take the most time will make sense only if those
processes contribute real value and/or if completing them more quickly will
permit other value-adding tasks to be completed in the time created through
efficiency.
Once you have your first
focus project selected, you will begin by creating a process map. This can be a
visual (e.g. on a whiteboard, sticky notes, PowerPoint or Excel) or a written
list, but the key here is to capture every single action or decision
that is made between the initiation and completion of the process.

Let’s take, for example, the
process of creating new expanded text ads in Google Ads.
Step 1: Decision
There are four primary means through
which I can create my ads:
- Create each ad
directly in the Google Ads interface, within the campaign and ad group of my
choosing - Create each ad in
the Google Ads Editor and post the changes to Google Ads - Draft the ads in
a spreadsheet and copy/paste to Google Ads Editor - Draft the ads in
a spreadsheet and bulk upload into Google Ads
Each of these will have its
own subsequent series of steps, and the decision will likely be based on how
many ads I plan to create.
If I am creating only a
single ad, then working directly in the Google Ads interface may be the most
efficient. However, ads are more frequently launched in batches, so it will often
be more efficient to build the copy in a spreadsheet and upload through the
Google Ads Editor.
Step 2: Detailed Process Map
Let’s say I have chosen
option #3 above and will be mapping the process for creating ads via Excel and
Google Ads Editor. I will need observe the process in action, either by going
through the steps myself or making note as someone else completes the task. I
then outline the basic steps that go into this process as:
Preparation
- Create new excel sheet and save with clear file name and date
- Label columns in row 1: Account (if multiple), Campaign, Ad Group, Labels, Headline 1, Headline 2, Headline 3, Description 1, Description Line 2, Path 1, Path 2, Final URL, Mobile Final URL (if any), and Tracking template (if any)
- Type or download and copy/paste desired Campaign and Ad Group names into the appropriate columns
Copy Creation
- Type Headline 1 and verify length using the =len()
function - Type Headline 2 and verify length using the =len()
function - Type Headline 3 and verify length using the =len()
function - Type Description Line 1 and verify length using the =len()
function - Type Description Line 2 and verify length using the =len()
function - Type Path 1 and verify length using the =len()
function - Type Path 2 and verify length using the =len()
function - Type or copy Final URL and verify correct page loads
- Type or copy Mobile Final URL and verify correct page
loads - Type or copy tracking template and proof for errors or
extra spaces - Type labels with identifier and date to distinguish ad
variations
Quality Assurance
- Check spelling on all ad copy
- Proof for appropriate capitalization
- Save excel file
- Send to client for approval (if needed)
- If not approved, make changes based on client feedback
- Check spelling and proof for capitalization
- Resend to client for approval
Upload
- After approval, reopen excel file and review that no
data has been lost - Open Google Ads Editor
- Open desired ad account(s)
- Download recent changes
- Navigate to Expanded Text Ads window
- Select “Make multiple changes”
- Copy/paste data from excel into Google Ads Editor
- Verify column names mapped correctly
- Process and review changes
- Resolve errors (if any)
- Select “Check changes”
- Resolve errors (if any)
- Select “Post”
Step 3: Make Value-Based
Decisions
Once the steps of the process
are mapped, I can look at the elements of each segment to determine which
actions are truly adding value and which are not. The goal is to minimize the amount
of time spent on non-value-adding elements.
For example, I may look at my
ad creation process and notice that team members are consistently spending
non-value-adding time on the Preparation phase, which is repeated with every
new set of ads created. I recognize that by reducing the amount of time spent
on Preparation, I can improve the efficiency of the entire process without
sacrificing any amount of value.
One answer might be learning how to build an ad copy proposal template in excel, which can then be opened and renamed (“Save As”) by each team member at the start of the ad creation process. Suddenly, the Preparation phase is reduced to a single step and those few minutes saved can be channeled toward another productive task.
Bottleneck (“DMAIC”) Analysis
Sometimes efficiency opportunities will be less clear than in the above example and require a bit more work to uncover. If you are an established group that already utilizes a curated toolbox of templates, automation (i.e. scripts, google alerts, bid rules, etc.), and have mastered the art of using excel for PPC, then a bottleneck analysis (or, the DMAIC approach) may be a better fit for you.
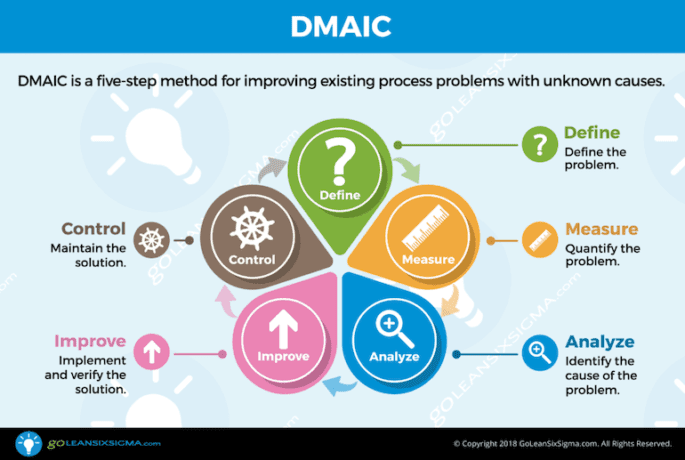
Step 1: Define
You will again start by
mapping or defining the steps that take place within your selected process. For
the sake of this process, you will want to group actions that take place
simultaneously or would be classified as a single “step” in the process.
However, understanding the distinct actions within each step will be necessary
as we get deeper into the analysis.
The end goal of this action
is a process map such as the one outlined above.
Step 2: Measure
Once you have your process
map outlined, you will begin to collect real data on the execution of the
procedure. In most cases, this will relate to the amount of time spent on each
step of the process. However, you should also document the number of errors or
revisions required, as those will equate to waste that could and should be
eliminated.
The end goal of this action
is a process map with an objective data set related to each step.
Step 3: Analyze
With data in hand, you can
now determine objectively which step(s) could be optimized in order to reduce
waste or variation. Your data should reveal if there are any steps frequently
being repeated (such as “(re)send to client for approval” or “resolve errors
(if any)” in the example above), or steps with significant variation in the
time required to complete. Any steps that serve as a bottleneck, due to either
variation or waste, are prime for optimization or elimination.
The end goal of this action
is to identify one or more bottlenecks, and the contributing factors to that
bottleneck, which can be improved for efficiency.
Step 4: Improve
As you might expect, once you
have identified the bottleneck issue, you must take action to resolve it. To
demonstrate, let’s say that I am looking to improve the process for updating
Facebook ad creative on behalf of a small enterprise client. After mapping the
steps in the process, I find two activities to be the largest bottlenecks
inhibiting my process flow: obtaining creative from the client and customizing
assets for non-feed placements.
To address the first
bottleneck, I calculate the amount of time, on average, it takes to get new
imagery from the client after making a request. I then determine how many
creative refreshes would ideally take place during that same amount of time.
This tells me how many sets of creative I need to request in order to receive
the imagery at approximately the time I will need it. My improvement decision
is to ask for 30% more imagery than needed during each request, which provides
cushion against potential bottlenecking in the future.
For the second bottleneck, I make
note that asset customization in Facebook must be completed for a single ad, so
bulk editing is not an option to improve efficiency. However, I also note that many
aspects of the customized creative are the same regardless of the ad set in
which it is placed. I determine that instead of creating ads in bulk and then
customizing them individually, I will create and customize a single ad, then
duplicate across ad sets where the customized creative matches. This allows me
to then bulk edit the standard elements (i.e. headline, landing page URL, tracking
parameters, etc.) without needing to complete the asset customization step for
each individual ad creative.
The end goal of this action
is to have a clear action plan that will eliminate waste or variation in your
observed bottlenecks.
Step 5: Control
The final step is to ensure
that the improvements implemented have the desired effect and do, in fact, improve
efficiency within your processes. If you note that the improvement plans are
causing additional delay, waste, or variation, you will need to return to step 1,
2, or 3 for a better understanding of the bottleneck contributors.
If you have completed all
steps effectively, however, you should find that your processes go more
smoothly and more quickly over time as the DMAIC benefits are reaped.
Closing Thoughts
This has been a very brief and high-level overview of lean six sigma practices within the narrow scope of PPC marketing. There is a wealth of additional information available across the web, and I encourage you to dive deeper if the ideas here are of interest to you.
I am eager to see more of these principles in action, so if you are a digital marketer who leverages lean six sigma in your own team management or practices, please reach out to me on Twitter or LinkedIn to share your perspective!
